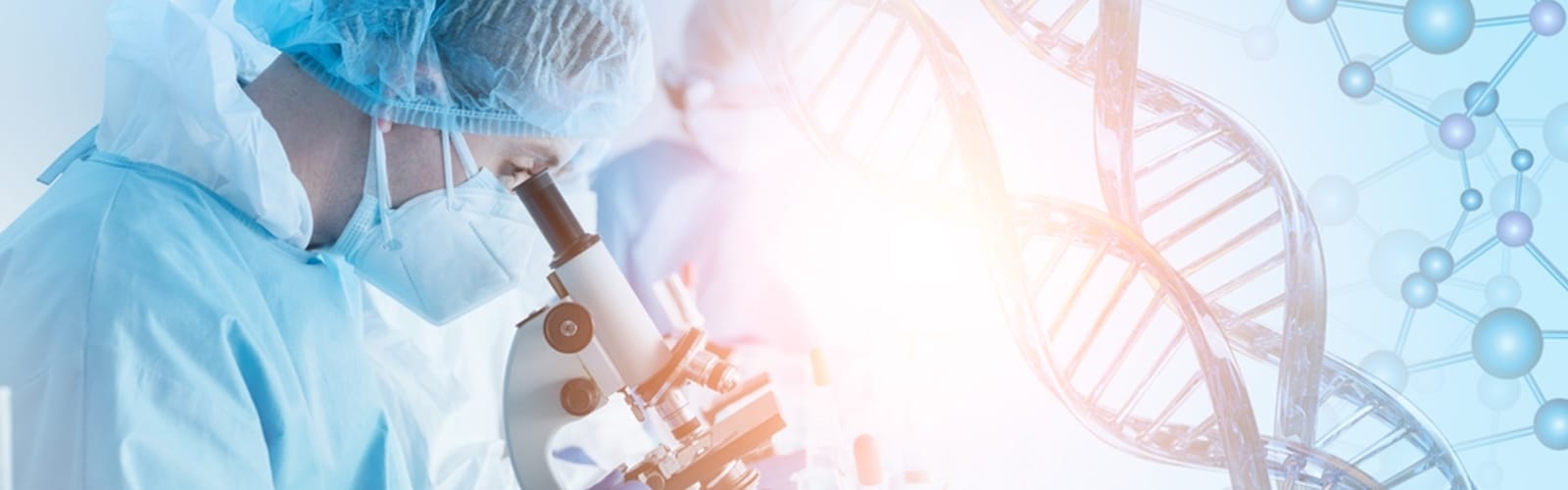


The gut “tube” is the interface between the outside and inside of the body. The digestive tract is over 30 feet long in an adult. This lining or gastrointestinal (GI) epithelium is the body’s greatest barrier and defense against microbes and other invaders. It is no wonder that 70% of our immune system resides in the gut. Intestinal epithelium have the fastest cell turnover in the body. New epithelium replaces the cells that are lost through digestion every 3-6 days. The GI epithelium also functions as a semi-permeable surface to absorb nutrients from food. Normally, the cells lining the gut are impermeable, forming tight junctions (see diagram). Digested food particles are actively carried through cellular pathways into the smaller blood vessels that lead to the liver and then to the tissues throughout the body. A compromised epithelium causes a breakdown of the intestinal barrier and disruption of these tight junctions. This leads to the passage of food particles, and pathogens such as bacteria and viruses, between the cells. What follows is inflammation, poor absorption of nutrients, immune dysfunction and Various diseases.
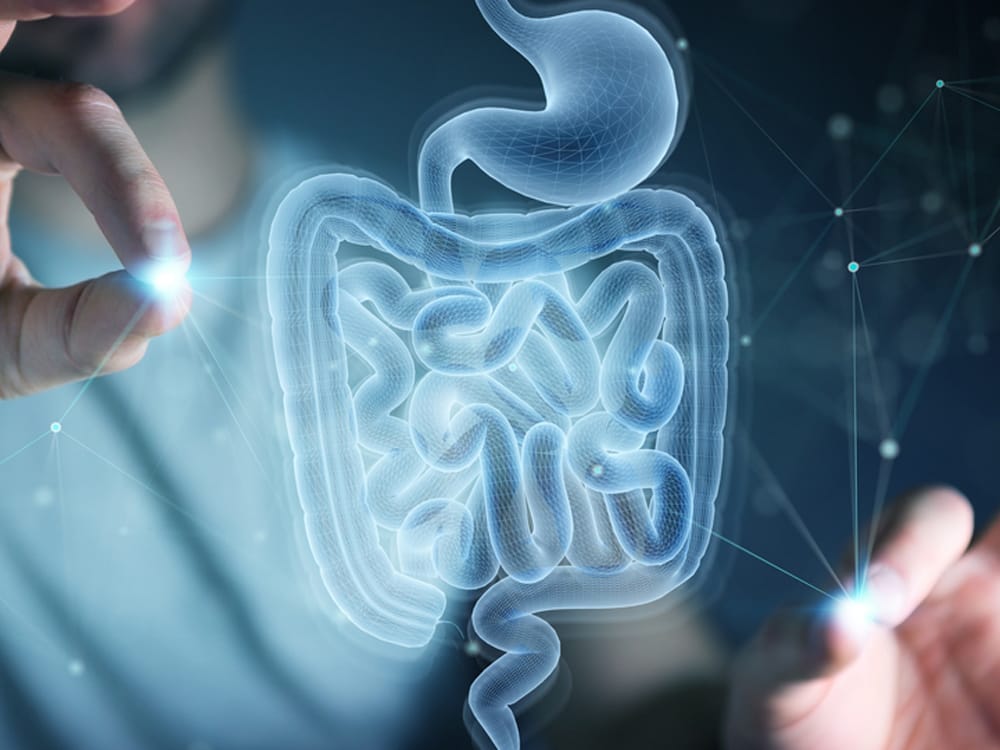
1.Lactulose-Mannitol Test
2.Zonulin test
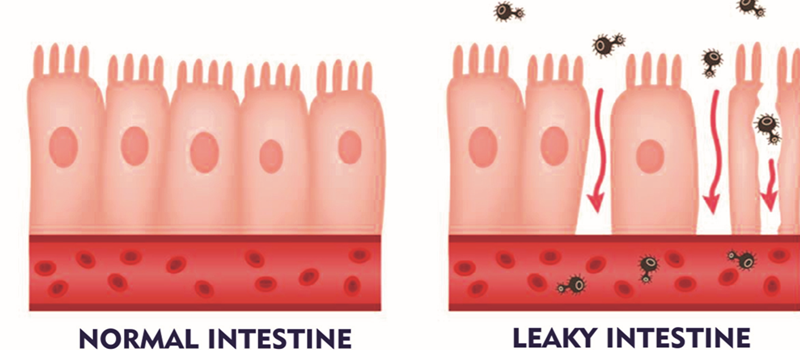
Following factors can initiate/aggravate Leaky gut to happen…



© 2025 Enactis. All Right Reserved.
Designed & Developed by  Innov Touch Technologies Pvt Ltd.
Innov Touch Technologies Pvt Ltd.